The final version of Version 6.0 of the open-source virtualization management platform Proxmox VE has been released. The new version based on Debian GNU/Linux 10 and comes with Linux Kernel 5.0, QEMU 4.0.0, LXC 3.1.0, Ceph 14.2 (Nautilus), ZFS 0.8.1, and Corosync 3.0.2.
What’s new in Proxmox VE 6
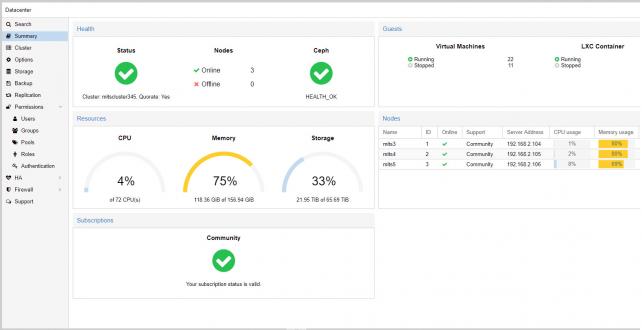
- Ceph Nautilus (14.2) and improved Ceph dashboard management: Proxmox VE allows to setup and manage a hyperconverged infrastructure with a Proxmox VE/Ceph-cluster. Version 6 integrates the features of the latest Ceph 14.2 release, and also brings many new management functionality to the web-based user interface. This includes: a cluster-wide overview for Ceph being displayed in the ‘Datacenter View’; a new donut chart visualizing the activity and state of the placement groups (PGs); the version of all Ceph services is displayed, making detection of outdated services easier; the configuration settings from config file and databases can be displayed; users can select the public and cluster networks in the web interface with a new network selector; encryption for OSDs can be activated easily during creation with a checkbox.
- Cluster communication stack with Corosync 3 using Kronosnet: with Proxmox VE 6.0 the cluster communication stack has been updated to Corosync 3 by which the on-the-wire format has changed. Corosync now uses unicast as default transport method. This provides a better control of failovers as different networks can now be prioritized. A new selection widget for the network is available in the user interface helping to choose the correct link address and preventing users from making typos.
- ZFS 0.8.1 with native encryption and SSD TRIM support: the new features for ZFS include enhanced security and data protection thanks to the added support for native encryption with comfortable key-handling by integrating the encryption directly into the `zfs` utilities. Encryption is as flexible as volume creation. TRIM support is included. The subcommand `zpool trim` notifies devices about unused sectors, thus TRIM can improve the usage of the resources and contribute to longer SSD life. Also checkpoints on pool level are available.
- Support for ZFS on UEFI and on NVMe devices in the ISO installer: the installer now supports ZFS root via UEFI, for example you can boot a ZFS mirror on NVMe SSDs. By using `systemd-boot` as bootloader instead of grub all pool-level features can be enabled on the root pool.
- QEMU 4.0.0: new QEMU functionalities are included in Promxox VE 6.0. Users can now use the web interface to live migrate guests with disks backed by local storage, and to set more VM CPU-flags. Support for more Hyper-V enlightenment has been added thus improving Windows performance in a virtual machine under QEMU/KVM.
-Custom Cloudinit configurations: Proxmox VE 6 brings support for custom Cloudinit configurations and lets users store it as Snippet. The command `qm cloudinit dump` can be used to get the current Cloudinit configuration as a starting point for extensions.
Other Notable Changes in Proxmox VE 6.0
- Automatic clean-up of old kernel images: the old kernel images are no longer marked as ‘NeverAutoRemove’ which helps to prevent problems when /boot is mounted on a small partition.
- Guest status display in the tree view: Additional states for guests (migration, backup, snapshot, locked) are shown directly in the tree overview.
- Improved ISO detection in the installer: the way how the installer detects the ISO has been reworked to include more devices, alleviating problems of detection on certain hardware.
- Pool level backup: it’s now possible to create a backup task for a whole pool. By selecting a pool as backup target instead of an explicit list of guests, new members of the pool are automatically included and removed guests automatically excluded from the backup task.
- Automatic rotation of the authentication key every 24h: by limiting the key lifetime to 24h the impact of key leakage or a malicious administrator are reduced.
- The Node view in the user interface provides a faster syslog view.
By using Proxmox VE 6 as an open-source alternative to proprietary virtualization management solutions, enterprises are able to centralize and modernize their IT infrastructure and turn it into a cost-effective and flexible software-defined data center.
Availability
Proxmox VE 6.0 is available for download at https://www.proxmox.com/downloads.
Checklist tool ‘pve5to6’: Users can check their installation before, during and after the upgrade process with the checklist tool ‘pve5to6’. It’s included in the latest Proxmox VE 5.4 packages and will provide hints and warnings about potential issues.
Distribution upgrades from Proxmox VE 5.4 to 6.0 should follow the detailed instructions as a major version of Corosync is present (2.x to 3.x). There is a three-step upgrade path for clusters where users first need to upgrade to Corosync 3, then upgrade to Proxmox VE v6.0, and finally upgrade the Ceph cluster from Ceph Luminous to Nautilus.
For detailed upgrade guides please see https://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Upgrade_from_5.x_to_6.0 and https://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Ceph_Luminous_to_Nautilus .
Distribution upgrades from a beta version of Proxmox VE 6.0 is possible with apt. It’s also possible to install Proxmox VE 6.0 on top of Debian Buster.
Proxmox VE is published under the free software license GNU Affero GPL, v3. Enterprise support is available from Proxmox Server Solutions on a subscription basis starting at EUR 79,90 per year and CPU. For more information, visit https://www.proxmox.com
Proxmox VE 6.0 released
What’s new in Proxmox VE 6
- Ceph Nautilus (14.2) and improved Ceph dashboard management: Proxmox VE allows to setup and manage a hyperconverged infrastructure with a Proxmox VE/Ceph-cluster. Version 6 integrates the features of the latest Ceph 14.2 release, and also brings many new management functionality to the web-based user interface. This includes: a cluster-wide overview for Ceph being displayed in the ‘Datacenter View’; a new donut chart visualizing the activity and state of the placement groups (PGs); the version of all Ceph services is displayed, making detection of outdated services easier; the configuration settings from config file and databases can be displayed; users can select the public and cluster networks in the web interface with a new network selector; encryption for OSDs can be activated easily during creation with a checkbox.
- Cluster communication stack with Corosync 3 using Kronosnet: with Proxmox VE 6.0 the cluster communication stack has been updated to Corosync 3 by which the on-the-wire format has changed. Corosync now uses unicast as default transport method. This provides a better control of failovers as different networks can now be prioritized. A new selection widget for the network is available in the user interface helping to choose the correct link address and preventing users from making typos.
- ZFS 0.8.1 with native encryption and SSD TRIM support: the new features for ZFS include enhanced security and data protection thanks to the added support for native encryption with comfortable key-handling by integrating the encryption directly into the `zfs` utilities. Encryption is as flexible as volume creation. TRIM support is included. The subcommand `zpool trim` notifies devices about unused sectors, thus TRIM can improve the usage of the resources and contribute to longer SSD life. Also checkpoints on pool level are available.
- Support for ZFS on UEFI and on NVMe devices in the ISO installer: the installer now supports ZFS root via UEFI, for example you can boot a ZFS mirror on NVMe SSDs. By using `systemd-boot` as bootloader instead of grub all pool-level features can be enabled on the root pool.
- QEMU 4.0.0: new QEMU functionalities are included in Promxox VE 6.0. Users can now use the web interface to live migrate guests with disks backed by local storage, and to set more VM CPU-flags. Support for more Hyper-V enlightenment has been added thus improving Windows performance in a virtual machine under QEMU/KVM.
-Custom Cloudinit configurations: Proxmox VE 6 brings support for custom Cloudinit configurations and lets users store it as Snippet. The command `qm cloudinit dump` can be used to get the current Cloudinit configuration as a starting point for extensions.
Other Notable Changes in Proxmox VE 6.0
- Automatic clean-up of old kernel images: the old kernel images are no longer marked as ‘NeverAutoRemove’ which helps to prevent problems when /boot is mounted on a small partition.
- Guest status display in the tree view: Additional states for guests (migration, backup, snapshot, locked) are shown directly in the tree overview.
- Improved ISO detection in the installer: the way how the installer detects the ISO has been reworked to include more devices, alleviating problems of detection on certain hardware.
- Pool level backup: it’s now possible to create a backup task for a whole pool. By selecting a pool as backup target instead of an explicit list of guests, new members of the pool are automatically included and removed guests automatically excluded from the backup task.
- Automatic rotation of the authentication key every 24h: by limiting the key lifetime to 24h the impact of key leakage or a malicious administrator are reduced.
- The Node view in the user interface provides a faster syslog view.
By using Proxmox VE 6 as an open-source alternative to proprietary virtualization management solutions, enterprises are able to centralize and modernize their IT infrastructure and turn it into a cost-effective and flexible software-defined data center.

Availability
Proxmox VE 6.0 is available for download at https://www.proxmox.com/downloads.
Checklist tool ‘pve5to6’: Users can check their installation before, during and after the upgrade process with the checklist tool ‘pve5to6’. It’s included in the latest Proxmox VE 5.4 packages and will provide hints and warnings about potential issues.
Distribution upgrades from Proxmox VE 5.4 to 6.0 should follow the detailed instructions as a major version of Corosync is present (2.x to 3.x). There is a three-step upgrade path for clusters where users first need to upgrade to Corosync 3, then upgrade to Proxmox VE v6.0, and finally upgrade the Ceph cluster from Ceph Luminous to Nautilus.
For detailed upgrade guides please see https://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Upgrade_from_5.x_to_6.0 and https://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Ceph_Luminous_to_Nautilus .
Distribution upgrades from a beta version of Proxmox VE 6.0 is possible with apt. It’s also possible to install Proxmox VE 6.0 on top of Debian Buster.
Proxmox VE is published under the free software license GNU Affero GPL, v3. Enterprise support is available from Proxmox Server Solutions on a subscription basis starting at EUR 79,90 per year and CPU. For more information, visit https://www.proxmox.com
Proxmox VE 6.0 released
